
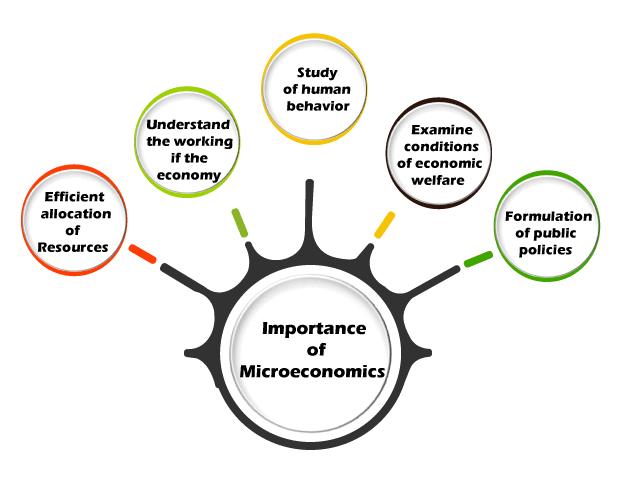
Macroeconomics is the study of the overall economic phenomena or the total economy. Macroeconomics | Definition A branch of economics that looks at economy in a broad sense and deals with factors affecting the national, regional, or global economy What should the company’s target audience be charged for its goods and services? What sources of capital would the company require to start or run the business? How many employees will be hired, and at what rate will they be hired? When should the firm expand, downsize, or shut down? It also specifies what and how many goods or products a firm must manufacture to be profitable. How do individuals decide how much money to set aside for unforeseen expenses? What mix of items and services best satisfies their requirements and preferences within their limited budget? The study of how individuals and households spend their money is known as microeconomics. In this case, demand is important in establishing the quantity and price of a product, as well as the price and quantity of related items (complementary goods) and replacement products, to make an informed decision about the allocation of scarce resources based on their alternative uses. It also provides the requirements for making the optimum use of resources to maximize production and social welfare. It determines how limited resources are allocated among individuals to satisfy their demands.
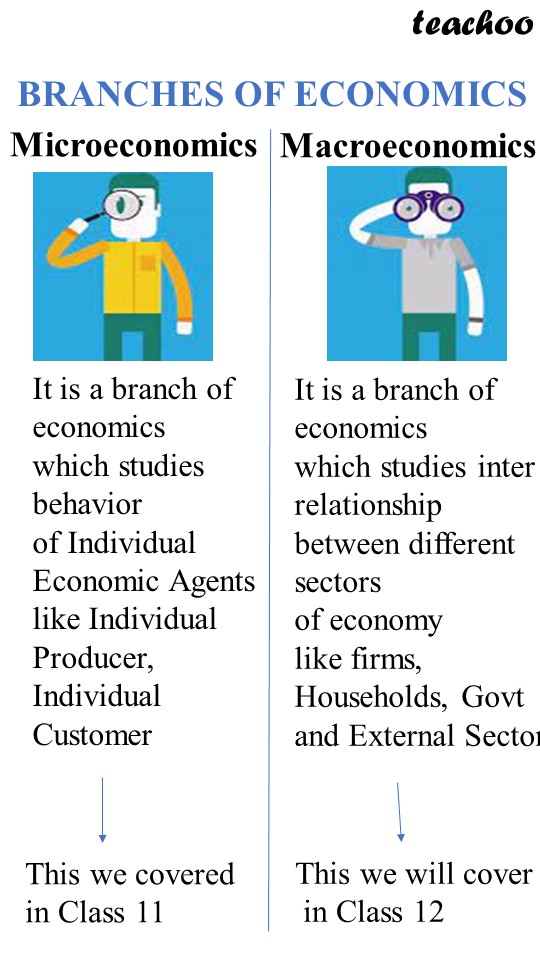
Micro is the study of the behavior and performance of individual economic players within the economy, such as consumers, families, industries, and businesses.

Microeconomics focuses on issues that affect individuals and companies and Macroeconomics focuses on issues that affect nations and the world economy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
